knee compression rotation test|positive knee tests : ODM •Therapist compresses the flexed knee joint and the menisci –by pushing the patient’s foot and tibia down into the table, followed by internal and external rotation of the tibia. Special Test: . WEBLinks icq. 3371 members. View Open in web. Don't have an ICQ yet? Download. Links icq. 3368 members. View .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da IT talent must be smart, agile, and ready to work when the moment strikes. .
The Apley grind or compression test is a physical examination maneuver first described by the British orthopedic surgeon Alan Graham Apley. It is commonly performed to .The KKU knee compression-rotation test for detection of torn meniscus had better rates of diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy than McMurray test. Therefore, the KKU knee .How to Interpret the Apley Compression Test. Positive Finding: A positive test occurs when pain or popping is noted with rotation during the compression test. Relief of symptoms with distraction or presentation of pain elsewhere in the . flex the knee and place a hand on medial side of knee, externally rotate the leg and bring the knee into extension. a palpable pop / click + pain is a positive test and can correlate with a medial meniscus tear.
•Therapist compresses the flexed knee joint and the menisci –by pushing the patient’s foot and tibia down into the table, followed by internal and external rotation of the tibia. Special Test: . The knee compression rotation test was developed by Sarachai et al (2007). To carry out this test the patient lies supine on the examining table. The knee is passively flexed .
The Apley test is a series of knee and lower leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. You might see it referred to as an Apley grind test or an .
To test the lateral meniscus, the tibia is rotated internally, and the knee is extended from maximal flexion to about 90 degrees; added compression to the lateral meniscus can be produced. The clinical diagnosis of meniscal tears has been found to be more accurate when combinations of tests are used. 3,9,13 Traditional maneuvers such as the McMurray test 16 . The knee compression rotation test was developed by Sarachai et al (2007). To carry out this test the patient lies supine on the examining table. The knee is passively flexed by grasping the patient’s ankle, with the other hand positioned over the joint line. Knee compression is created by pushing the tibia onto the femur, then the tibia is . This position eliminates any rotation of the hip, allows the knee to fall into a valgus position and causes internal rotation of the tibia on the femur. . Rotatory Intability of the Knee: its pathogenesis and a clinical test to demonstrate its presence. The journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, american volume, 1968; 50-A, No.2:211-225.
Results: The KKU knee compression-rotation test had sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy for detection of meniscal tear as 86.27, 88.23, and 86.76% respectively, which superior to McMurray test that was 70.59, 82.35, and 73.53%. In addition, the KKU knee compression-rotation test had false positive and false The KKU knee compression-rotation test for detection of torn meniscus had better rates of diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy than McMurray test. OBJECTIVE The purpose of the present study was to compare the sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic accuracy of a new test, named "KKU Knee Compression-Rotation Test", with the most widely used .Then, fixate the tested leg with your own leg and bring the knee into 90° of flexion. While you give distraction, perform lateral rotation of the tibial and medial rotation. You are looking for excessive rotation compared to the other side or discomfort. Then, repeat the same procedure, while you are giving compression.Orthopedic Assessments Made Easy: The Knee Joint Assessment. The Orthopedic Assessments Made Easy orthopedic guide book is written by Dr. Rina Pandya, a professional Doctor of Physiotherapy with more than 23 years of experience in the field, who now is a senior lecturer of Physiotherapy at the University in England after years of work in the India, USA and Oman.
Finally, the knee compression-rotation test is where the tibia is compressed and rotated with respect to the femur. 19 All these more recent maneuvers were introduced with evidence of high sensitivity and specificity but have not supplanted the original tests, nor does consensus exist regarding a composite evaluation for meniscal injury. 5 The .
Pain with active compression test. Increased Q-angle. Inspection. Skin. scars. trauma. erythema. Swelling. . External rotation recurvatum test. . flex the knee and place a hand on medial side of knee, externally rotate the leg and bring the knee into extension. a palpable pop or click is a positive test and can correlate with a medial . Meniscal testing is based on trying to subluxate the torn meniscus by applying compression and rotation forces on the knee and palpating the snap when it jumps back to the normal position. Joint Line Tenderness. . This angle is determined in the contralateral knee. In this test, the injured knee is put in the same angle and the patient is . The Apley Compression Rotation test is performed for meniscal tears of the knee. Originally, the distraction portion of the exam was thought to potentially .The Apley grind test or Apley test is used to evaluate individuals for problems in the meniscus of the knee. [1] The Apley grind test has a reported sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 87%. [2] . Lateral rotation tests for medial implications (meniscal during compression and ligamentous when distracting the tibia) and medial rotation .
The purpose of the present study was to compare the sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic accuracy of a new test, named "KKU Knee Compression-Rotation Test", with the most widely used .Medial meniscus and lateral meniscus of the knee; Diagram by BruceBlaus – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Link. . When testing the lateral meniscus the tibia starts the manoeuvre in external rotation. Test Movement. . Apley’s Compression/Grinding Test; Share this: Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window) Compression rotation test. The examiner imparts a compressive force from the elbow through the long axis of the humerus as the shoulder is rotated in an attempt to grind the labrum and elicit pain. Myers et al 21 recently described a test termed the “resisted-supination external-rotation test.” The test is performed in the supine position .In order to perform the Compression-Rotation Test have your patient in supine position, while the examiner is standing on the patient’s affected side. . This test is positive in case of catching or snapping, similar to the McMurray test in the knee. 21 OF THE MOST USEFUL ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Name * Email *
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.The FABER (Patrick’s) Test stands for: Flexion, Abduction and External Rotation. These three movements combined result in a clinical pain provocation test to assist in diagnosis of pathologies at the hip, lumbar and sacroiliac .
The Posterolateral External Rotation (Drawer) Test is a combination of the posterior drawer and external rotation tests: with the knee flexed at 30° and then at 90°, the tibia is forced posteriorly and in external rotation subluxating the tibia. If subluxation occurs at 30° but not at 90° an isolated PLC injury is supposed, while if .
Purpose: To assess the contribution of the sacroiliac joint to an apparent leg length discrepancy. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: The examiner grasps the patient's legs above the ankles and fully flexes them, then extends them. The examiner then compares the two medial malleoli to see if a difference in position is present. Have the patient sit up, while keeping the .
Lien étude KKU Knee Compression Rotation Test: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17487126/🌟 Bienvenue sur la chaîne Osteo-Upgrade ! 🌟📚 Prêt à approfondir vo.
The KKU knee compression-rotation test had sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy for detection of meniscal tear as 86.27, 88.23, and 86.76% respectively, which superior to McMurray test that was 70.59, 82.35, and 73.53%. In addition, the KKU knee compression-rotation test had false positive and false negative rates of 11.76 and 13. .A comprehensive overview of meta-analyses and systematic reviews concluded that the Lachman test is the only test able to rule in or out a knee disorder [Decary, 2017]. The Lachman test was found to be an accurate test to rule in or out an anterior cruciate ligament injury [ Decary, 2017 ], although another systematic review found it to have .
The McMurray test is a series of movements to check your symptoms and range of motion (how far you can move your knee joint). The test is simple and includes the following steps: You’ll lay on your back. Your provider will bend your knee to 90 degrees perpendicular to the rest of your body (about where it would be if you were in a seated .
compression test adapter for nozzle hole

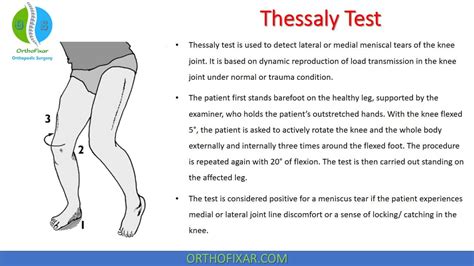
What is the Apley test? The Apley test is a series of knee and lower leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. You might see it referred to as an Apley grind test or an Apley compression test. Providers use these names interchangeably to refer to the same test.Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of a labral tear or acromioclavicular lesion. Test Position: Sitting or standing Performing the Test: The patient is instructed to place the shoulder into 90 degrees of flexion and 10 degrees of adduction. Next, the arm is actively internally rotated so the thumb is pointing downward. The instructor then applies a inferior directed force (into .The FADIR test, standing for flexion, adduction and internal rotation test, is designed to evaluate the piriformis, gluteal muscles and hip joint as a source of pain. The patient is typically supine but can be laying on their contralateral side. The examiner passively flexes the hip into 90 degrees of flexion, while adducting and internally .Purpose: To assess for a lesion in the meniscus. Test Position: Standing. Performing the Test: Have the patient stand on the test leg with the knee bent to 20 degrees of flexion (the opposite leg is flexed behind the patient). The patient may place his/her hands on the hands of the examiner for balance during the test. The patient then rotates the knee medially and laterally .
provocative knee tests
positive knee tests
webLaboratório Biopse, Fortaleza, Brazil. 338 likes · 1 talking about this · 572 were here. Laboratório com tradição e excelência em exames de patologia e medicina laboratorial.
knee compression rotation test|positive knee tests